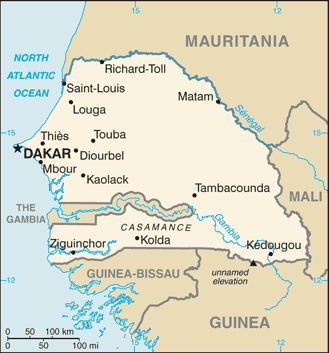
Senegal, officially the Republic of Senegal, is a country south of the Sénégal River in western Africa. It owes its name to the river that borders it to the East and North and that originates from the Fouta Djallon in Guinea.
Senegal is externally bounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the west, Mauritania to the north, Mali to the east, and Guinea and Guinea-Bissau to the south. Gambia River, which bisects Senegal’s territory. The capital Dakar lies on the Cap-Vert peninsula, the westernmost point of continental Africa.
Senegal is one of only a handful of countries to have a near-enclave within its borders—the small nation of The Gambia in the interior, which has a 740 km border with Senegal. The Gambia penetrates more than 320 km into Senegal. About 500 km off the coast, in the Atlantic Ocean, lie the Cape Verde Islands.
Senegal has been held up as one of Africa’s model democracies. It has an established multi-party system and a tradition of civilian rule.
Although poverty is widespread and unemployment is high, the country has one of the region’s more stable economies.
